Steel Wire Rope
- Dawson Group Ltd. - China Manufacturer, Supplier, Factory

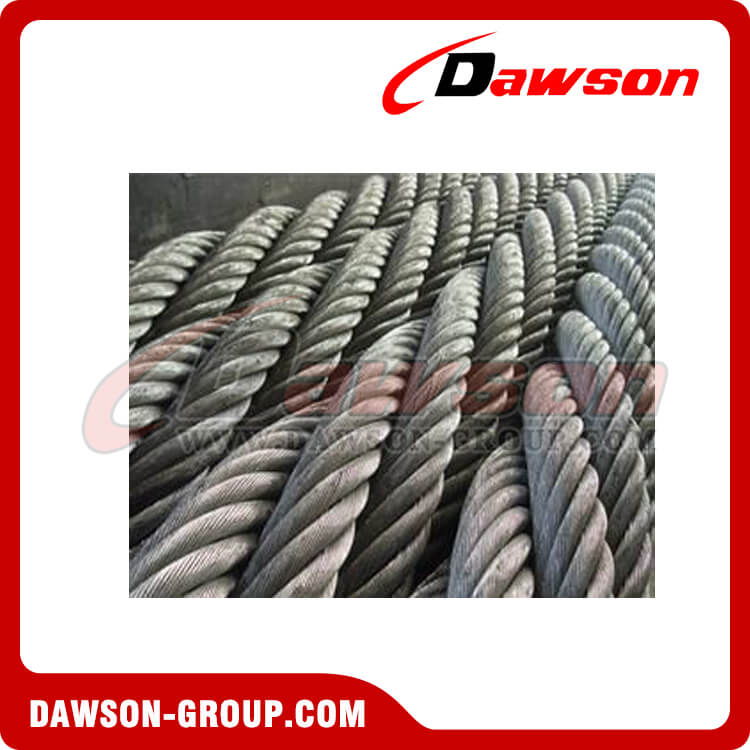
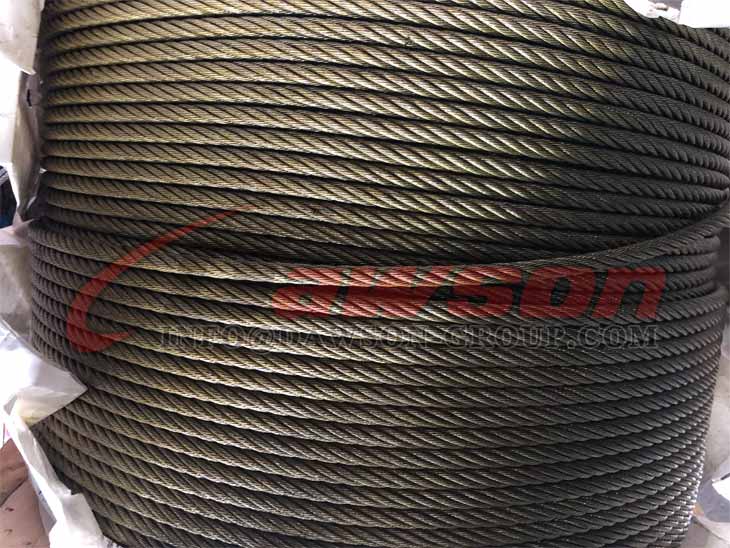
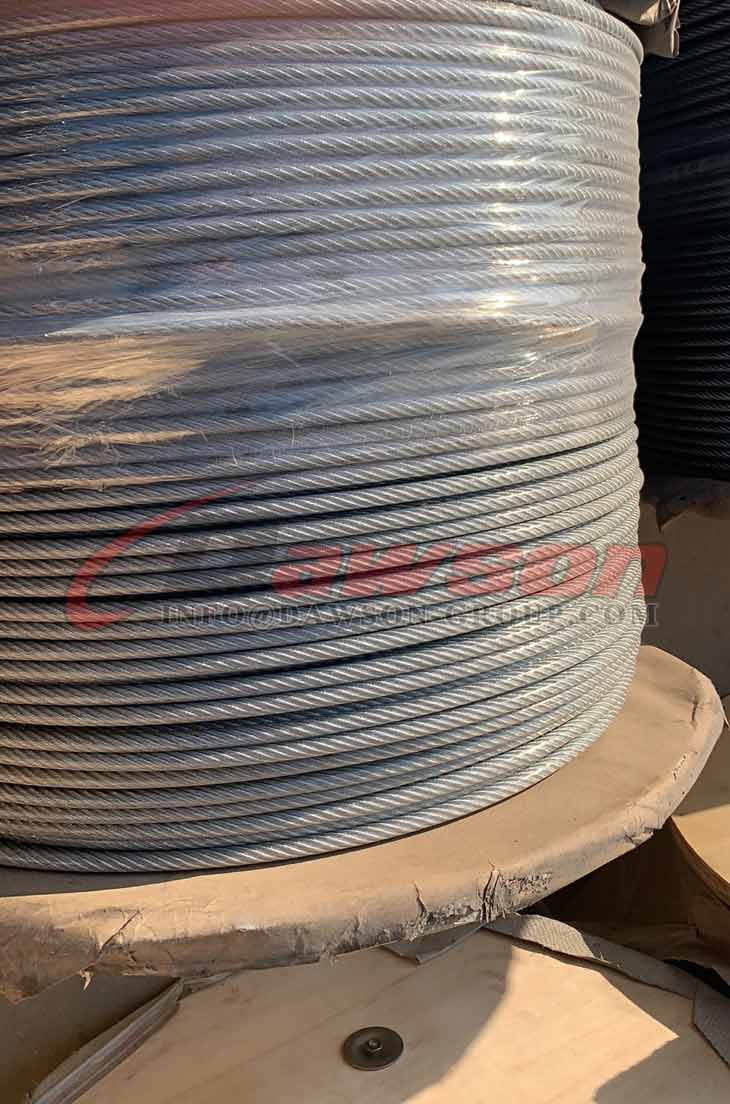
Steel Wire Rope


General Information on Wire Ropes
Wire rope is made of plaiting strands of wire – normally medium carbon steel –into a thick cable. The strands are formed around a core. The strands in wire ropes are made of wore twisted together. Strands with smaller diameter wires are less abrasion resistant and more fatigue resistant. Strands made with thicker length of wore are more abrasion resistant and less fatigue resistant.
Steel Wire Ropes
Sizes : From 3mm to 80mm
Surface Finish : Galvanized and Ungalvanized
Core : IWRC, FC and WSC
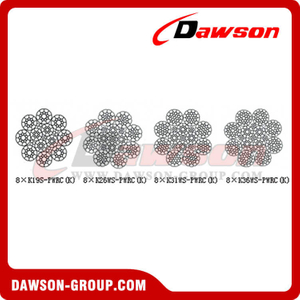
Typical Wire Constructions : 6x37, 6X19, 18x7 and more
Tensile Strengths : 1960 N/mm2 (EIPS) and 2160 N/mm2 (EEIPS)
Lay of Wire Rope
 |  |
| Left-hand ordinary lay (LHOL) wire rope (close-up). Right-hand lay strands are laid into a left-hand lay rope. | Right-hand Lang's lay (RHLL) wire rope (close-up). Right-hand lay strands are laid into a right-hand lay rope. |
The lay of a wire rope describes the manner in which either the wires in a strand, or the strands in the rope, are laid in a helix.
Left and Right Hand Lay
Left hand lay or right hand lay describe the manner in which the strands are laid to form the rope. To determine the lay of strands in the rope, a viewer looks at the rope as it points away from them. If the strands appear to turn in a clockwise direction, or like a right-hand thread, as the strands progress away from the viewer, the rope has a right hand lay. The picture of steel wire rope on this page shows a rope with right hand lay. If the strands appear to turn in an anti-clockwise direction, or like a left-hand thread, as the strands progress away from the viewer, the rope has a left hand lay.
Ordinary, Lang's and Alternate Lay
Ordinary and Lang's lay describe the manner in which the wires are laid to form a strand of the wire rope. To determine which has been used first identify if left or right hand lay has been used to make the rope. Then identify if a right or left hand lay has been used to twist the wires in each strand.
| Ordinary lay | The lay of wires in each strand is in the opposite direction to the lay of the strands that form the wire. |
| Lang's lay | The lay of wires in each strand is in the same direction as the lay of the strands that form the wire. |
| Alternate lay | The lay of wires in the strands alternate around the rope between being in the opposite and same direction to the lay of the strands that form the wire rope. |
| Regular lay | Alternate term for ordinary lay. |
| Albert's lay | Archaic term for Lang's lay. |
| Reverse lay | Alternate term for alternate lay. |
| Spring lay | This is not a term used to classify a lay as defined in this section. It refers to a specific construction type of wire rope. |
Construction and Specification
 | In the above example, each individual wire is arranges around a central wire to form a 7-wire strand. Six of these strands are formed around a central core to make a wire rope. The rope is specified as 6x7 (6/1) – i.e. six strands each of seven wires. |
The specification of a wire rope type – including the number of wires per strand, the number of strands, and the lay of the rope – is documented using a commonly accepted coding system, consisting of a number of abbreviations.
This is easily demonstrated with a simple example. The rope shown in the figure "Wire rope construction" is designated thus: 6x19 FC RH OL FSWR
| 6 | Number of strands that make up the rope |
| 19 | Number of wires that make up each strand |
| FC | Fiber core |
| RH | Right hand lay |
| OL | Ordinary lay |
| FSWR | Flexible steel wire rope |
Each of the sections of the wire rope designation described above is variable. There are therefore a large number of combinations of wire rope that can be specified in this manner. The following abbreviations are commonly used to specify a wire rope.
| Abbr. | Description |
| FC | Fibre core |
| FSWR | Flexible steel wire rope |
| FW | Filler wire |
| IWR | Independent wire rope |
| IWRC | Independent wire rope core |
| J | Jute (fibre) |
| LH | Left hand lay |
| LL | Lang's lay |
| NR | Non-rotating |
| OL | Ordinary lay |
| RH | Right hand lay |
| S | Seale |
| SF | Seale filler wire |
| SW | Seale Warrington |
| SWL | Safe working load |
| TS | Triangular strand |
| W | Warrington |
| WF | Warriflex |
| WLL | Working load limit |
| WS | Warrington Seale |
Terminations

RHOL wire rope terminated in a loop with a thimble and talurit splice
The end of a wire rope tends to fray readily, and cannot be easily connected to plant and equipment. A number of different mechanisms exist to secure the ends of wire ropes to make them more useful. The most common and useful type of end fitting for a wire rope is when the end is turned back to form a loop. The loose end is then fixed by any number of methods back to the wire rope.
Thimbles
When the wire rope is terminated with a loop, there is a risk that the wire rope can bend too tightly, especially when the loop is connected to a device that spreads the load over a relatively small area. A thimble can be installed inside the loop to preserve the natural shape of the loop, and protect the cable from pinching and abrasion on the inside of the loop. The use of thimbles in loops is industry best practice. The thimble prevents the load from coming into direct contact with the wires.
Wire Rope Clamps (DOG CLAMPS)
A wire rope clamp, also called a clip, is used to fix the loose end of the loop back to the wire rope. It usually consists of a u-shaped bolt, a forged saddle and two nuts. The two layers of wire rope are placed in the u-bolt. The saddle is then fitted over the ropes on to the bolt (the saddle includes two holes to fit to the u-bolt). The nuts secure the arrangement in place. Three or more clamps are usually used to terminate a wire rope.
Swaged terminations
Swaging is a method of wire rope termination that refers to the installation technique. The purpose of swaging wire rope fittings is to connect two wire rope ends together, or to otherwise terminate one end of wire rope to something else. A mechanical or hydraulic swager is used to compress and deform the fitting, creating a permanent connection. There are many types of swaged fittings. Threaded Studs, Ferrules, Sockets, and Sleeves a few examples.
Sockets
A socket termination is useful when the fitting needs to be replaced frequently. For example, if the end of a wire rope is in a high-wear region, the rope may be periodically trimmed, requiring the termination hardware to be removed and reapplied. An example of this is on the ends of the drag ropes on a dragline. The end loop of the wire rope enters a tapered opening in the socket, wrapped around a separate component called the wedge. The arrangement is knocked in place, and load gradually eased onto the rope. As the load increases on the wire rope, the wedge become more secure, gripping the rope tighter.
Eye Splice
The ends of individual strands of this eye splice used aboard a cargo ship are seized with natural fiber cord after the splicing is complete. This helps protect seaman's hands when handling.
An eye splice may be used to terminate the loose end of a wire rope when forming a loop. The strands of the end of a wire rope are unwound a certain distance, and plaited back into the wire rope, forming the loop, or an eye, called an eye splice.
|  |
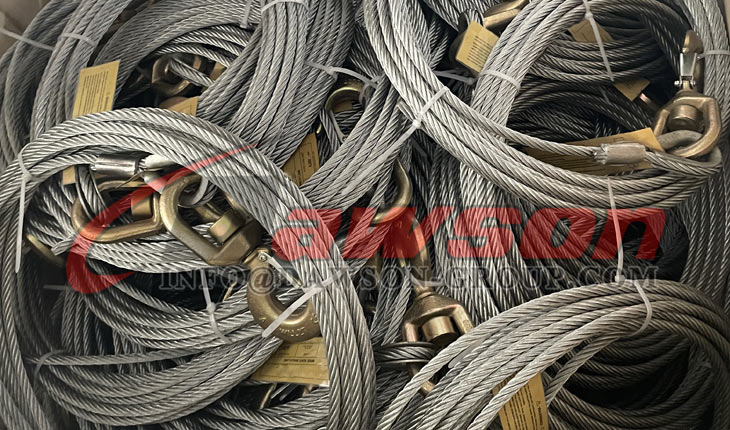
Dawson Steel Rope
ISO9001 quality
Application:avation,crane,lift,transportation,fishery,machinery,electricity,etc.
Steel Wire Rope: Galvanized, ungalvanized
Diameter : from 2mm to 100mm
Normal tensile strength: from 1470MPA to 2160MPA
Steel Wire Rope: Galvanized, ungalvanized
Diameter : from 2mm to 100mm
Normal tensile strength: from 1470MPA to 2160MPA
Rope core: with FC, 7FC, IWS or IWR
Packing: wooden wheel, as customer required
Main construction:
| Construction | application |
6×7
6×9W | Cable car, belt conveyer, cable way drawing and slope well winching |
6×12
6×15 | Tugboat, goods net, haulage, binding |
| 6×19 | Lifting machine, fishery, heat-moving machine and general machine
|
6×24
6×24S
6×24W | tugboat, fishery, cargo net, floating woods, binding, loading |
| 6×37 | Crane, hoist, loading, refloatation, fishery, vertical well balance |
6×25Fi
6×29Fi
6×31SW
6×36SW
| Lifting, hoisting and dragging.
The rope with steel core may be used under the shock load, heated and squeezed condition. |
6×+NF
6×7+IWS
6×19+NF
6×19+IWS | For important machinery and instrument |
| 6×19S+FC | For elevator |
Related Products :






















Hot Tags: steel cabon China exporter, high quality wire rope, wholesale wire rope, low price wire rope, wire rope, carbon steel wire rope, wire ropesteel wire rope China manufacturer, Steel Wire Rope China supplier, Steel Wire Rope China factory, Wire Rope China supplier, Wire Rope China manufacturer Wire Rope Breaking Testing Machine:


Application of Steel Wire Rope:

Steel Wire Rope Catalogue Download:

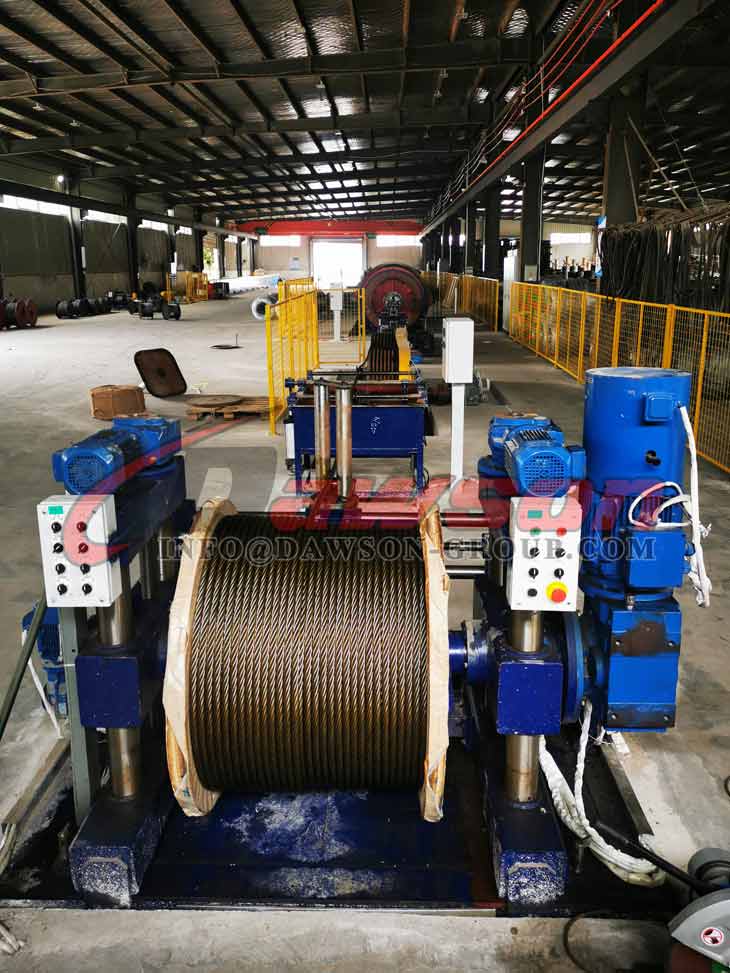
Factory and Package Show:












 English
English